Difference between revisions of "The Ramp API"
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
The RPL Scripting Portal is especially useful for building and testing scripts. However since the RPL language contains no control structures, the Javascript RPL Portal provides a richer programming environment for scripting Ramps. The console (left window) in this portal is a complete Javascript runtime extended by an object bound to '''$$'''. This object contains functions corresponding to each of the RPL operators, plus the function '''dispatch''', which can be used to invoke a sequence of RPL commands as strings. Both usages are shown in Fig. 5, which executes the same script as in the previous section but using a loop structure to achieve greater economy. The use of '''$$.dispatch''' shows how command can be sequenced in one line. | The RPL Scripting Portal is especially useful for building and testing scripts. However since the RPL language contains no control structures, the Javascript RPL Portal provides a richer programming environment for scripting Ramps. The console (left window) in this portal is a complete Javascript runtime extended by an object bound to '''$$'''. This object contains functions corresponding to each of the RPL operators, plus the function '''dispatch''', which can be used to invoke a sequence of RPL commands as strings. Both usages are shown in Fig. 5, which executes the same script as in the previous section but using a loop structure to achieve greater economy. The use of '''$$.dispatch''' shows how command can be sequenced in one line. | ||
The '''Go''' button provides a convenient way of executing a script. If the entry point of the script is defined as the function '''go()''', clicking the button will invoke the script, | The '''Go''' button provides a convenient way of executing a script. If the entry point of the script is defined as the function '''go()''', clicking the button will invoke the script, so that typing into the console is not necessary. | ||
As with RPL scripts, JS Scripts can be saved and loaded, and any script left in the editor will be part of the Ramp settings. | As with RPL scripts, JS Scripts can be saved and loaded, and any script left in the editor will be part of the Ramp settings. | ||
Revision as of 18:46, 17 February 2022
The Ramp API (Application Programming Interface) uses a simple language called RPL to manage and operate Ramp simulations and retrieve data for remote processing. It can be used in three ways: directly, through the RPL Scripting Portal (S On/Off button); indirectly through the Javascript RPL Portal (JS On/Off button); and remotely from other platforms such as the R Statistical language.
Using RPL
RPL is simple bytecode with instructions for adjusting parameter values, controlling runs, and retrieving data. There are RPL instructions to perform virtually any task a user might perform directly by changing sliders, adjusting runtimes or saving data to CSV files. RPL scripts are saved as part of the saved Ramp settings and workspace settings.
The RPL Portal contains left and right windows. The left window is an RPL interpreter, which executes a sequence of RPL commands. The right window is an editor for creating scripts that can be loaded and run by that interpreter. Scripts can be loaded in their entirety and run, or executed line by line. Improperly formed commands are not executed and there is no error report.
The Logging window (below the interpreter), when enabled, shows the actions taken by the system for each command. It is especially useful when using the API remotely.
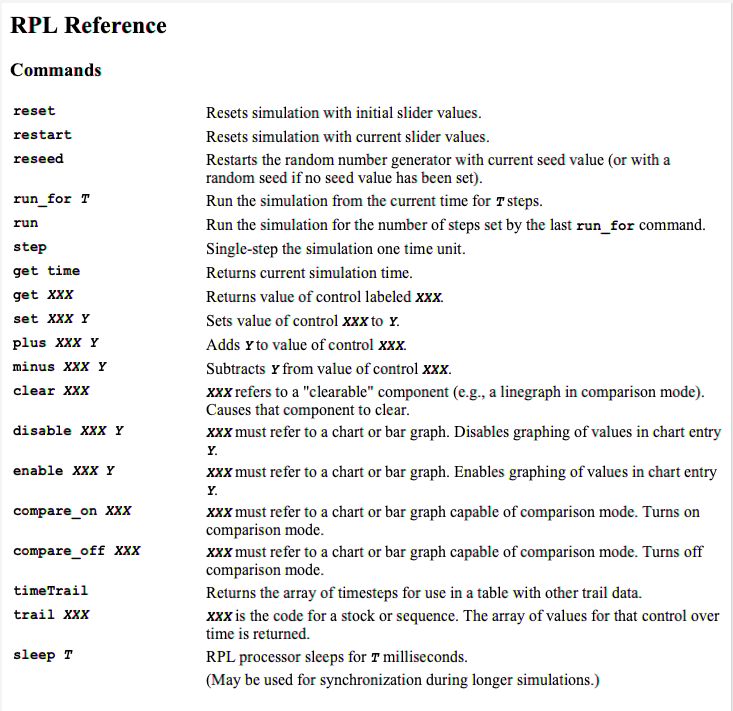
The RPL Reference sheet can be viewed using the Command Reference button on the RPL Scripting Portal. It is shown below in Fig 2.
Each instruction in RPL consists of an op code followed by 0 or more arguments. The XXX arguments refer to Airport Codes, as described in the Ramp User Guide. Fig. 3 reproduces the Notes on the reference sheet.
Scripts entered into the RPL Scripting Portal can saved and reloaded.
Example
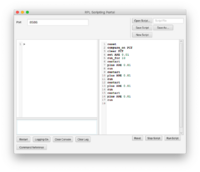
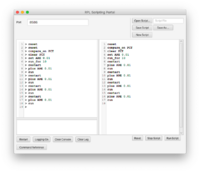
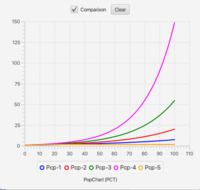
One particular use of the Scripting Portal is for managing multiple runs with different parameters. The example shown in Fig. 4a is a script for the Pop Ramp[1] that flips the graph into comparison mode and runs the simulation 5 times, incrementing the rate parameter by 0.01 each time. Clicking Run Script executes the script line-by-line (Fig 4b) and produces the graph shown in Fig 4c.
Note: the operation restart rather than reset is used between runs. Reset returns the parameters to their values before the script was run.
Using Javascript
|
The RPL Scripting Portal is especially useful for building and testing scripts. However since the RPL language contains no control structures, the Javascript RPL Portal provides a richer programming environment for scripting Ramps. The console (left window) in this portal is a complete Javascript runtime extended by an object bound to $$. This object contains functions corresponding to each of the RPL operators, plus the function dispatch, which can be used to invoke a sequence of RPL commands as strings. Both usages are shown in Fig. 5, which executes the same script as in the previous section but using a loop structure to achieve greater economy. The use of $$.dispatch shows how command can be sequenced in one line.
The Go button provides a convenient way of executing a script. If the entry point of the script is defined as the function go(), clicking the button will invoke the script, so that typing into the console is not necessary.
As with RPL scripts, JS Scripts can be saved and loaded, and any script left in the editor will be part of the Ramp settings.
R Integration
- ↑ One of the example Ramps that you can download from Numerus