Difference between revisions of "Component Guide I: Atomic Components"
(→State) |
(→State) |
||
| Line 88: | Line 88: | ||
*'''Dimension'''. Used with [[Array-Based Modeling]]. | *'''Dimension'''. Used with [[Array-Based Modeling]]. | ||
*'''Unit'''. Optional specification of a unit for this State value. | *'''Unit'''. Optional specification of a unit for this State value. | ||
;Examples | ;Examples | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
Revision as of 16:32, 13 March 2018
Overview
Nova models are constructed out of components, which are visual tokens that are placed on the Model Canvas.
To place a component on the model canvas:
- Press the left mouse button on the desired component in the menu obtained from the component tab.
- Drag the component from the component menu onto the model canvas.
- When prompted, provide a component name (a default name will be provided if you choose not to provide one).
A new component requires two actions to integrate it into the model:
- Connections must be made to components with which this component will interact; and
- The new component must be programmed; in the simplest case, this involves providing a component formula that defines the value represented by this component. Specific programming tasks for each component type will be described below.
Component Types
- Atomic Components
- Tranditional systems dynamic components State (subdivided into Stock Stock+Flow, Sequence, Sequence+Flow, and Store), Flow, and Term; along with Command and Event.
- Containers
- Nova containers consist of Chips and 5 types of aggregators; a Chip holds a single instance of Capsule, used as a submodel while aggregators hold multiple Capsule instances, possibly of different types. Each aggregator type implements a different topology for its elements. The aggregator components are AgentVector, CellMatrix, NodeNetwork, SimWorld and NetWorld.
- Controls and Displays
- These include Table, Linechart, Scatterchart, Barchart, Histogram, Slider, Spinner and Toggle.
- Special
- These are special purpose components consisting of Code Chip and Comment.
- Plugins
- These are extensions to the component set and have various functions.
Component Properties
Each component has an associated Properties Pane (PropPane) that provides the means for programming the component (and in some cases specifying connections.) The PropPane is opened by selecting the component. PropPanes allow you to define the value represented by a component, set pin connections, determine what is displayed (in the case of Graphs and Tables), calibrate (in the case of Sliders and Spinners) and set any other property required by the component. Specific properties are part of the component descriptions below.
Component Formulas
Most components require a formula or program to specify their values. This formula is a NovaScript expression or sequence of expressions entered into a text area on the PropPane. Component value formulas can make use of the underlying Javascript language to build somewhat complex algorithms for computing the value [1], however long and complex computations are becodeer relegated to code chips or global method definitions.
Simple Formulas
In the simplest case this will be a constant number or string, or an arithmetic formula. Formulas may reference other value-producing components such as States or Terms, and may also reference any of the global elements known as Primitives.[2]
- Examples
Formula Notes 27x + 22 * PIPIis a primitive constant.COS(2*PI*x)COSis a primitive operator
Important: the caret (^) operator is not supported in Javascript for exponentiation. Instead, use Math.pow; e.g. 2^3 becomes Math.pow(2, 3).
Programmatic Formulas
You may wish to compute the component value over several steps involving conditionals and/or loops. NovaScript permits this according to the following schematic:
statement; statement; .... statement; value
In other words, you may include a sequence of statements, separated by semi-colons, which include local variable declarations and any legal Javascript statement. Numerus will interpret the last entry in that sequence as the value.
- Example
var x = 0; for (var i = 1; i <= 100; i++) x = x + i; xThis formula will produce
5050
Atomic Components
State
The State component comes in 5 versions.
| Symbol | Component | Description |
|---|---|---|
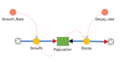
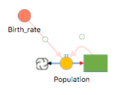
| Stock | A Stock represents a value that is changing over time. Changes to the stock are specified using one or more Flows, which are connected to it. Flows are either inflows or outflows, which respectively represent values being added to or subtracted from the current stock value. The value of a Stock at the end of each time step is equal to the value at the previous time step, plus the total inflow (i.e. the total flow value flowing into the stock) minus the total outflow (i.e., the total flow value flowing out of the stock). Stock values must be numerical. | |
 |
Stock+Flow | A stock with a single inflow, for convenience. May be preferred when modeling differential equations. |
| Sequence | A Sequence is a type of Stock in which the total flow value replaces rather than adds to the current stock value. A sequence value may be any legal NovaScript data type. | |
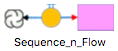 |
Sequence+Flow | A sequence with a single inflow, which is generally all that is required. |
| Store | A Store is a type of Stock without flows. It is used to hold values that may not require updating at each timestep of the simulation. Stores are used by Commands and Code Chips to store values across simulation timesteps. A Store may be any legal NovaScript data type. Previous versions of Numerus (i.e. Nova 2) called these Local Variables. |
- Properties
- Initial Value. The initial value is expressed as a component formula.
- Non-Negative. Check this box if the State must be non-negative. Negative values are mapped to 0. This option is not available for Stores.
- Full History. Specifies how long values are retained by this Stock. If selected, values are maintained for the entire length of the simulation; otherwise they are only kept for the previous 100 time units. Check this box only if your simulation requires a longer or complete history of the Stock's value.
- Dimension. Used with Array-Based Modeling.
- Unit. Optional specification of a unit for this State value.
- Examples
Flow
Notes
- ↑ Discussion of Javascript is beyond the scope of this document; see Javascript References for more information about programming in Javascript.
- ↑ A list of primitive operators and constants appears under the Primitives tab.