Difference between revisions of "Component Guide IV: Plugins"
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
*'''Next'''. A tab is provided for each state. Code implementing the transition from that state is entered into each tab. The rules for this code are identical to the rules specifying the value of a [[Component_Guide_I:_Atomic_Components#Component_Formulas|Component Formula]]. The result produced by the code must be another state. | *'''Next'''. A tab is provided for each state. Code implementing the transition from that state is entered into each tab. The rules for this code are identical to the rules specifying the value of a [[Component_Guide_I:_Atomic_Components#Component_Formulas|Component Formula]]. The result produced by the code must be another state. | ||
|[[File:discretestateprop.png]] | |[[File:discretestateprop.png]] | ||
|} | |||
==Tabulator== | |||
[[File: tab.png|left]] | |||
A tabulator is a special component that works with an aggregator in which a constituent (agent, cell, node) has either a Discrete State component or uses a Sequence to model a discrete state. The tabulator counts the number of elements in each state and outputs the totals on separate pins, primarily for graphing or displaying in a table. The states are expected to be consecutive numbers such as 0, 1, 2, etc. The sequence need not start at 0. (The sequence will, or course, always start at 0 if a Discrete State component is used.) | |||
<br clear="all"> | |||
{| | |||
| | |||
==Properties== | |||
*'''Size'''. The number of possible states. This determines the number of output pins on the Tabulator. | |||
*'''Base Value'''. States run from Base Value through Base Value + Size - 1. | |||
|[[File:tabprop.png]] | |||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 19:26, 2 October 2018
Plugins are additional components that provide special functionality. In future releases it will be possible for the user to create and add plugins of his/her own creation (a plugin writers guide is planned). We also anticipate future releases with plugin sets designed for specific application domains.
The current release of Numerus includes 2 plugins, which are described below.
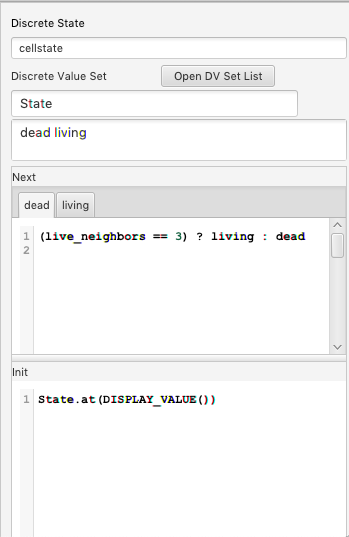
Discrete State
A Discrete State is an alternative to a Sequence in which a fixed number of named discrete states serve as possible values. A discrete state is initialized with one such value, and transitions are structured based on the current value.
Properties
|
|
Tabulator
A tabulator is a special component that works with an aggregator in which a constituent (agent, cell, node) has either a Discrete State component or uses a Sequence to model a discrete state. The tabulator counts the number of elements in each state and outputs the totals on separate pins, primarily for graphing or displaying in a table. The states are expected to be consecutive numbers such as 0, 1, 2, etc. The sequence need not start at 0. (The sequence will, or course, always start at 0 if a Discrete State component is used.)
Properties
|
File:Tabprop.png |
