Quick Programming References
Designer Architecture
Numerus Designer is a platform for building and running simulations. A simulation requires a set of state values and a clock that iterates through a sequence of time units. The simulation uses the current state at a given point in time to determine the next state. In Designer, the state is factored across a set of interacting Components managed by a container called a Capsule.
Capsules
- The fundamental structural unit for Designer is the Capsule.
- A Capsule is comprised of a set of interacting elements called Components.
- Each Capsule actually acts as a class, or blueprint for creating one or more instances of its Component set. This is true except for the top-level Capsule, for which there is only a single instance.
- When starting a new project, you are provided with an empty canvas on which to design the top-level Capsule. Many models only require a top-level Capsule. Additional Capsules are used to implement Cells and Agents in cellular and/or agent-based models. Capsules are also used to define new Components for use in other Capsules.
Components
- Components compute useful functions or serve as containers for Agents or Cells.
- Components are either stateful or stateless. Stateful Components manage some part of the state. State values determined by these components are carried from the current time step to the next. Stateless Components compute values from the current state of the simulation that are used to determine the next values for stateful Components, but these values are not retained across the transition from one time unit to the next.
- Most Components need to be programmed; i.e., provided with values or code that determine their behavior. Within that code may be references to the current values of other Components. The simplest Component programming calls for one or more constant values, however for most Components a code segment using the Java language is required.
- User-defined code segments are called squibs. Each squib either computes and returns a value, or performs a state change. The bulk of Designer programming is in writing squibs.
A complete guide to Designer Components can be found here.
Overview
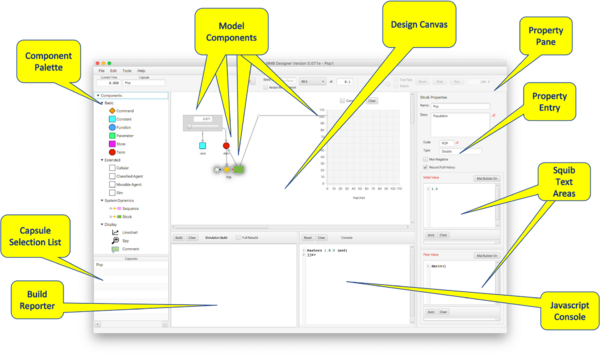
Platform
- Design Canvas
- Site of model construction.
- Capsule Selection List
- Choose Capsule for display on the Design Canvas.
- Component Palette
- Drag Components from here onto the Design Canvas.
- Model Components
- Components selected for inclusion in the current Canvas
- Property Pane
- Appears for selected Component; facilitates Component property definitions.
- Property Entry
- Simple property values entered into text fields or selected with Checkboxes or Radio Buttons.
- Important: when entering simple numerical or textual values into a text field be sure to press return when completing the entry; otherwise the entry may not register with the system.
- Squib Text Areas
- Text areas containing Squib definitions.
- Build Reporter
- Console used to report the result of a build.
- Javascript Console
- Interactive command processor that can retrieve Component values; useful for debugging.
Command Bar
- Current Model Time
- Shows elapsed time as simulation progresses
- Current Capsule
- Shows the name of the Capsule being edited.
- Studio Launch
- Launches the current model into Numerus Studio for further development. (Note: the red script "R" appearing in property panes indicates data used to specify properties important to Numerus Studio.)
- RNG Seed and Reset Mode
- Including a seed value resets the random number generator to produce the same sequence of random numbers. A reset is indicated by a flash of yellow in the text field. This reset occurs by default with a double click on the Reset Button. Checking Restart RNG on Reset causes an RNG reset each time the simulation resets.
- Integration Mode
- Indicates the integration method used by Stocks. Choices include RK (Runge-Kutta) 4, Euler and Discrete (Euler with a DT value of 1).
- DT
- Model time interval between iterations of the simulation.
- Model Run Speed
- Adjusts the running speed. Has no effect on model time.
- Model Operation Buttons
- Reset, Stop and Run control the execution of the simulation. Pressing Run after Stop continues the simulation from the current model time.
- Remaining Model Time
- This text field is initialized for the length of the run, and decreases as the run continues. When a run is completed, pressing Run will initiate a new run for the same length of time.
Programming Squibs
Introduction
By far the most extensive programming required to specify a model is providing content to various squibs required by different Components. Simple components (e.g., Stocks, Sequences, Terms, Parameters, etc.) generally have one or two squibs, while more complex components (e.g., Cellular, Movable Agent, Classified Agent, Sim, etc.) require numerous squibs to detail their behavior. In this section we provide general information about writing squib code that applies to squibs throughout the Component set. (Some familiarity with writing Java code is expected.)
A runnable simulation must but built by clicking the Build button located above the Build Reporter. This process compiles the squib source code and creates an object called an RCapsule (runnable Capsule) which does the actual execution. The Build operation can be performed at any point during the construction of the model, and you are advised to build after each complete squib definition so that errors can be caught early.
Java data consists of base types (int, float, etc.) and object types. Objects use fields to hold state data and define methods, which are code segments, to manipulate their own data and that of other objects.
Designer provides a rich set of Primitive Operators or primops to facilitate computation and define Component state. A complete list of primops appears here.
Java is statically typed language and so proper typing rules must be adhered to. Designer uses only familiar base types (integers, reals, strings) and their arrays, plus a few simple internally-defined types to specify coordinates. The types used in Designer are as follows[1]:
- Byte, Short, Integer, Long
- Respectively 1, 2, 4 and 8 byte integer values.
- Float, Double
- 32 and 64 bit floating point (i.e., real) values
- Boolean
- The values true and false
- Char, String
- Character and String types.
- Void
- The constant null, representing the empty value for any object.
By far, the most common types used are Integer, Double and String.
Squib Types
Squib code resembles some or part of a method definition, depending on the squib type. Squibs are compiled to executable code during the build process. Any squib errors are displayed in the Build Reporter. You are advised to rebuild the simulation after completing each squib.
Components use 4 different squib types, depending on what is required by the Component. Squib types are color coded as shown in the following descriptions. Squib labels will use these colors to indicate the type of squib required.
Function
- Defines a function transforming input values to output values. The function may also use primops to change the Component's state. This squib has one of the following forms:
- (Type arg, ... Type arg) -> result
- (Type arg, ... Type arg) -> {Statement; Statement; ... return result}
- Use the first of these if your result can be computed with a single statement. If a sequence of statements is required, it must be enclosed in brackets and include a return statement. The return can appear anywhere and more than once so long as the code segment always terminates with a return (otherwise the compiler will reject the squib).
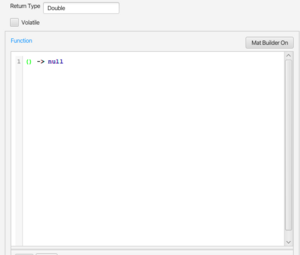
- The Function squib is notably used in the Function Component. A new Function Component will look as follows:
- Note that a return type must be specified (volatility will be explained below). The
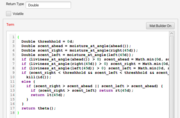
() -> nullis a reminder of the requirements of the squib. Here are 2 examples, corresponding respectively to the 2 formats shown above. Note that the first does not require a semicolon at the end of the line; and the second has 2 calls to return from different branches of the conditional.
- Fig 4. Two Function Squibs
Supplier or Term
- A Supplier squib is like a function of no arguments -- its format corresponds to the right hand side of the Function squib.
- result
- {Statement; Statement; ... return result}
- Supplier squibs are by far the most common squibs used by the Designer. They compute values based on the current state of other Components and return them for use by their Components. Supplier squibs may simply compute a value without affecting the system's state, or may use a primop to change state in the process of computing that value.
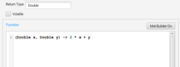
- The Term Component is defined with a single Supplier squib. A new Term will look like this
- The "0.0" is a reminder that the squib must return a value. Here are 2 examples showing the respective types.
- Fig 6. Two Supplier Squibs
Command
- Command squibs are like functions of no arguments that do not return values. They take the form of the second version of Supplier squibs, but omitting the brackets.
- Statement; Statement; ... Statement;
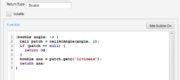
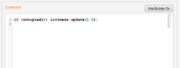
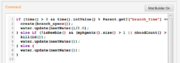
- Command squibs are the second most common squibs used by Designer. They manipulate the state of the system through primops and state-changing calls to other Components. The Command Component is defined with a single Command squib. A new Command will look like this
- Note that the squib can be empty since it is not required to do anything. In the first one, a state change occurs through the update call to a store. The second also performs Store updates and is concerned with the birth and death of agents. These topics are discussed elsewhere.
- Fig 8. Two Command Squibs
Hybrid
- A Hybrid squib is a cross between the Function and Supplier types, where specific input and output types are required. A Hybrid squib is like a Function in that it accepts one or more inputs; however the inputs are supplied by the Component, and the squib need only return a value of the expected output type using the format of a Supplier squib. In doing so it may refer to the input values while computing its result.
- A hybrid squib can be found in the Cell (and Agent) property pane, used to define the Actors used for particular row-column (or Agent ID) values.
- Note that like the Function squib, input values are specified, but in the header of the squib. The return type, in this case String, is shown on the right-hand-side of the header. The programmer need only write the body of the function in one of the formats of the Supplier squib, but may reference the variables row and col in the computation.
- Here is an example where the squib is used to determine the Actor for each agent in a Movable Agent Component.
- This code will be executed for each Agent created at the start of the simulation, with the variable id bound each time to a different value.
Referencing Components from Squibs
Components may be value-producing functions of 0 or more arguments. Alternatively a component may have executable methods. Any component in a Capsule can reference any other Component in that Capsule (including itself) using the Component's name. For example, the flock model contains a Function called turn_at_most defined by:
(Double n, Double maxturn) -> {
Double newTheta = normalize(n);
if (Math.abs(newTheta) > maxturn)
newTheta = signum(newTheta) * maxturn;
return newTheta;
}
The Term cohesion invokes the Function with a function call using the Component's name:
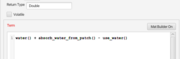
turn_at_most(turn_toward_me(), max_cohere_turn_rad())
The calls turn_toward_me and max_cohere_turn_rad refer respectively to a Term and a Constant, both of which have Supplier squibs and so are executed with 0 arguments
How to Continue
- Visit the Component Guide to learn about individual Components.
- Visit the Primop Guide to learn about the available Primops.
- ↑ Primitive versions of these (byte, short, int, long, float, double) can be used, however all primitive operators are typed using the equivalent Wrapper classes Byte, Short, Integer, etc.)